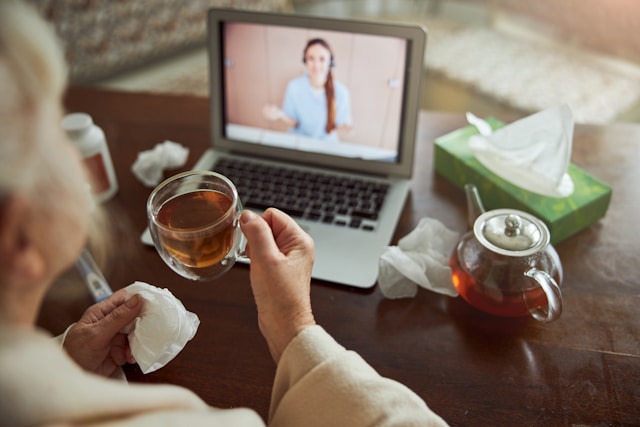
Telemedicine, the use of telecommunication technology to provide healthcare services remotely, has seen an unprecedented rise in recent years. This digital revolution in healthcare is breaking down traditional barriers to access, offering patients the convenience of receiving care from their homes, and presenting new models for how medical services are delivered and received. This article explores the growth of telemedicine, its benefits, challenges, and its impact on the future of healthcare.
Telemedicine: A Closer Look
At its core, telemedicine leverages technology—video calls, messaging, digital monitoring tools—to connect patients with healthcare providers. From routine check-ups to mental health services, telemedicine covers a broad spectrum of healthcare needs, making it an incredibly versatile tool for both patients and doctors.
Driving Forces Behind Telemedicine’s Growth
Several factors have contributed to the rapid adoption of telemedicine:
- Technological Advances: Improvements in internet connectivity and the ubiquity of smartphones have made telemedicine more accessible than ever.
- Healthcare Needs: An aging population and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases have demanded more flexible healthcare solutions.
- Pandemic Acceleration: The COVID-19 pandemic necessitated the adoption of remote healthcare practices to maintain social distancing, significantly accelerating telemedicine’s growth.
Benefits of Telemedicine
- Improved Access to Care: Telemedicine extends healthcare services to rural and underserved communities, overcoming geographical barriers.
- Convenience and Efficiency: Patients can receive care without the need to travel, wait in lines, or take time off work, making healthcare more convenient and efficient.
- Cost Reduction: By reducing the need for physical office visits, telemedicine can lower healthcare costs for patients and reduce overhead for providers.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Digital tools in telemedicine encourage patients to take an active role in their health management, improving outcomes.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, telemedicine faces several challenges:
- Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues: Varying regulations across regions and complexities in insurance reimbursement can hinder telemedicine’s implementation.
- Digital Divide: Access to the necessary technology and reliable internet remains a barrier for some populations, potentially widening health disparities.
- Privacy and Security: Ensuring the confidentiality and security of patient data in digital formats is paramount, requiring robust cybersecurity measures.
The Future of Telemedicine
Looking ahead, telemedicine is poised to become an integral component of healthcare delivery. The focus will likely shift towards improving the quality of remote care, integrating telemedicine with traditional healthcare models, and leveraging data analytics for better health outcomes. Future advancements may include more sophisticated remote monitoring technologies, AI-driven diagnostics, and personalized medicine approaches facilitated through telemedicine platforms.
Conclusion: Telemedicine’s Transformative Potential
Telemedicine represents a significant shift in how healthcare can be delivered and accessed. Its rise reflects a broader move towards a more digital, patient-centered healthcare system. While challenges remain, the potential of telemedicine to improve healthcare access, reduce costs, and make healthcare more personalized and efficient is undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the ways in which we engage with and benefit from telemedicine, shaping the future of healthcare for generations to come.